Soft Tissue Grafting
When people hear ‘grafting’, many things spring to mind—most of them quite scary, and few of them accurate.
With education being at the core of Dr. Caudry’s practice, we thought it best to take some time to educate you and the rest of our readers on the world of gum grafting. By the time you’re done reading this your understanding of periodontal surgery will have deepened, your misconceptions will have withered away, and your faith in Dr. Caudry and co. will have strengthened.
Before we explore periodontal surgery, let’s first look at why someone requires such a surgery.
When Your Gums Recede
Gum recession is a widespread condition that many people live with, without even realizing it!
Gum recession refers to the fading away of the gum tissue that surrounds the teeth. The gum tissue may look like it has been pulled back rather than having faded. This will sometimes give people the impression that you have ‘long’ teeth. Those teeth of yours aren’t any longer than before, it’s just that more of the tooth’s root is exposed than usual.
Gum recession has other drawbacks beyond slightly changing the look of your smile. Gums can recede to the point where the root of the tooth is exposed. When that happens, there are greater risks than just seeming like you have long teeth. When a tooth’s root is exposed it can be extremely sensitive to hot and cold foods as well as sugar. The more a tooth is exposed, the more chances there are for unwanted bacteria buildup. If you’re not proactive about tooth care, that bacteria could affect the surrounding tissue and lead to many problems.
Gum recession, if left untreated, can also lead to loosening of your teeth. If unwanted bacteria or periodontal disease is left untreated, gum pockets deepen, and teeth become loose.
What Causes Gum Recession?
Your gums may begin to recede for a variety of reasons.
For some, the cause—ironically—is brushing too hard. You might think there is no such thing as brushing too hard but think again. Aggressive or incorrect brushing can cause a tooth’s enamel to wear away and the gums to recede.
Overall poor dental care is another cause. Failing to floss, brush your teeth, or use antibacterial mouthwash can lead to a variety of problems. While all these things are important, what’s equally important is that you perform each task properly. Improper flossing can do as much harm as good.
Smoking, as we all know, is responsible for many problems. The use of cigarettes and other tobacco products often lead to the development of plaque which can lead to gum recession.
How to Fight Gum Recession
When your gums have receded to the point that you have developed swollen gums, loose teeth, big cavities or chronic bad breath, it is time to do something about the problem. If you were to visit your local dentist, they would inform you of your receding gums. Before long you might just find yourself speaking to a certified periodontist about soft tissue grafting.
What Is Soft Tissue Grafting?
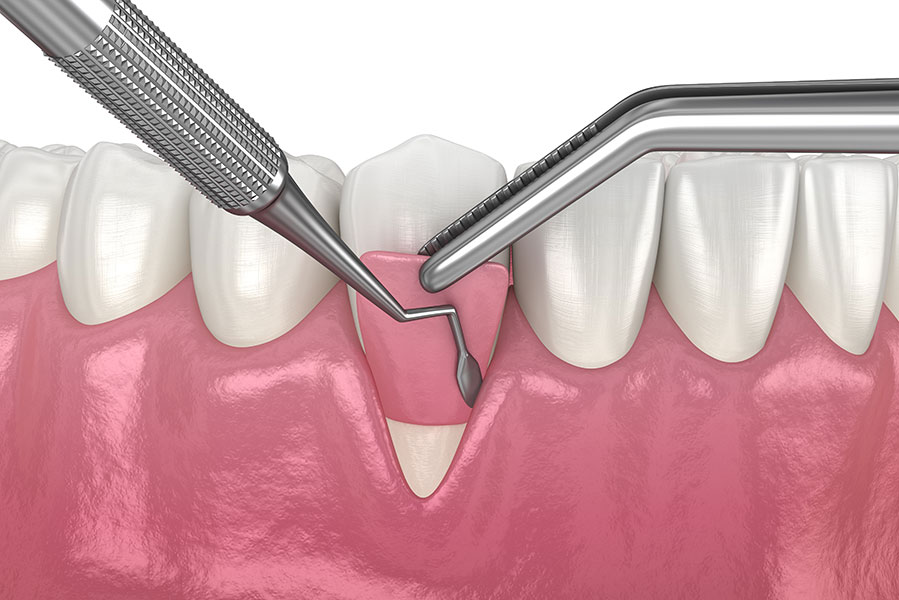
Soft tissue grafting is a minimally invasive procedure performed to combat gum recession. The main goal of soft tissue grafting is to either thicken the existing gum tissue or cover the exposed root in order to prevent further loss of gum tissue. The tissue used for the graft is usually taken from the roof of your mouth and stitched to the gum tissue surrounding the root. Though this might sound gruesome, it is painless, minimally invasive, and holds few risks for the patient.
The Benefits of Soft Tissue Grafting
There are many benefits to be had with soft tissue grafting. Some of these include:
- Comfort: Gum grafts can eliminate much of the pain and discomfort caused by gum recession. With the exposed root covered, hot and cold foods can once again be enjoyed. What’s more, the health of the gum area improves dramatically!
- Appearance: Though it is often recommended by periodontists for issues related to gum recession, you may also seek it out to improve your smile. Because soft tissue grafting is all about repairing the gum line, it will inadvertently make your teeth have the appearance of being smaller.
- Improved Health: The problems associated with gum recession (such as periodontal disease) can destroy your teeth and gum tissue rapidly. Gum grafts and a combination of proper dental care can put a stop to tissue loss, bone loss, and further issues.
The Connective Tissue Graft
There are several types of soft tissue grafts. One is the connective-tissue graft. By far the most common graft method, this one is used to treat root exposure. During this procedure, an incision is made into the roof of the patient’s mouth. A piece of tissue (known as subepithelial connective tissue) is removed from underneath the incision and stitched onto the exposed root’s surrounding gum tissue.
The Free Gingival Graft
Like the connective-tissue graft, the free gingival graft requires tissue from the roof of the mouth. However, this tissue doesn’t come from underneath the top layer of skin. Instead, the tissue comes from the top layer of flesh itself. This method is most often used when an individual’s gum tissue is very thin and only needs to be thickened.
The Pedicle Graft
With this approach, the periodontist creates a flap of tissue near the recessed area and uses that flap to cover it. For this procedure to be successful the patient needs plenty of healthy gum tissue surrounding the recessed area.
Recovery from Soft Tissue Graft
Before you are sent home, your dentist will give you specific instructions to ensure your gums heal correctly. You’ll be asked not to floss or brush the repaired area, and you’ll likely be given a special mouth wash to help fight plaque buildup. For a week or two following the procedure, you should expect to maintain a diet of soft and cool foods such as eggs, yogurt, pasta, and well-prepared vegetables.